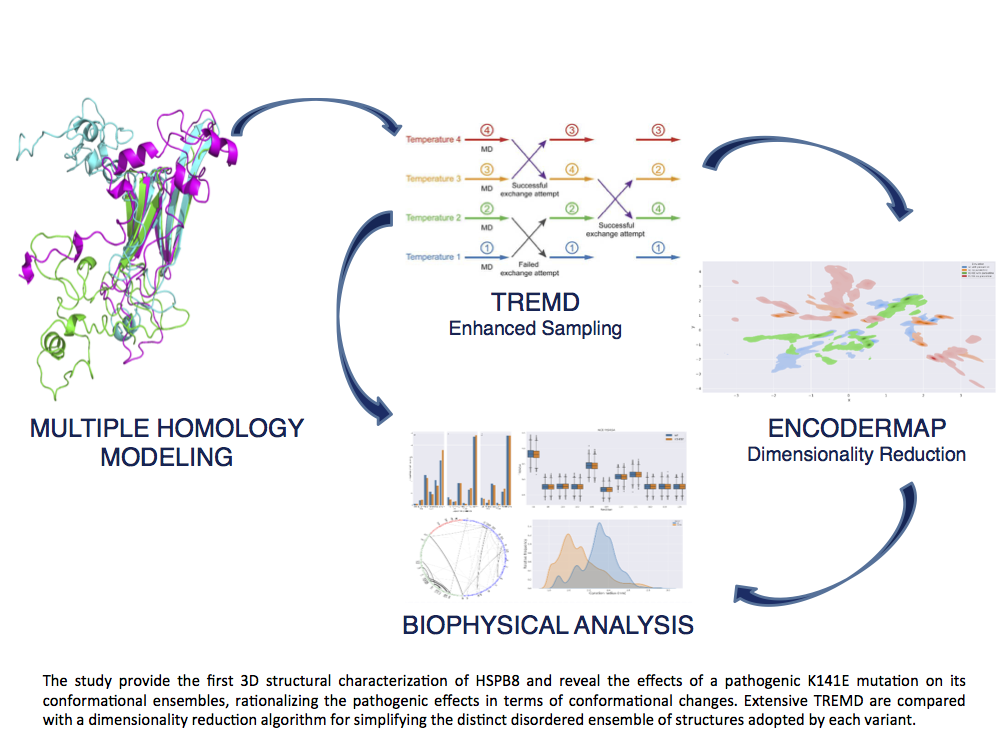
Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDPs) are widely represented and play a key role in many fundamental biological processes. The Heat Shock Protein B8 which is part of the protein quality control system that avoids the accumulation in cells of dangerous aggregates of misfolded structures. Its pathogenic mutant K141E, is related to distal motor neuropathy. In general, the onset of many degenerative diseases can be traced back to the malfunctioning of some IDP.
The main goal of our project is to establish a workflow that uses state-of-the-art deep learning algorithms to integrate data from simulations and experiments in an innovative tool for the exploration of the functionality of IDP. Detailed knowledge of this kind is an essential requisite for the development of the next generation of drugs, designed at a molecular level to precisely fulfill a predetermined objective.
| People | Giorgia Brancolini*, Ciro Cecconi, Daniele Montepietra |
| Keywords | IDP, Deep Learning, Artificial Intelligence, Alzheimer |
| Methods, techniques | Autoencoders, Temperature Replica Exchange MD, Homology Modelling, AlphaFold |
| Collaborations | University of Iceland; UNIMORE |
| Publications | |
| D. Montepietra, C. Cecconi, G. Brancolini Combining enhanced sampling and deep learning dimensionality reduction for the study of the heat shock protein B8 and its pathological mutant K141E RSC advances 12 (49), 31996-32011 | |
| D. Montepietra, G. Tesei, J. M. Martins, M. B. A. Kunze, R. B. Best, K. Lindorff-Larsen FRETpredict: A Python package for FRET efficiency predictions using rotamer libraries bioRxiv 2023.01.27.525885; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.27.525885 |